Managing a business today means handling sales, finance, HR, projects, and data across multiple tools. Not to forget the hidden cost of using multiple tools. This often leads to data gaps, delays, and poor visibility.
An ERP system solves this by bringing all core business functions into one platform. It connects teams, processes, and data, giving leaders a real-time view of business performance.
For business owners and decision makers, this means faster decisions, better control, and fewer errors. You spend less time managing systems and more time growing the business.
Modern ERP systems are built for SMBs as well as enterprises. They are cloud-based, flexible, and scalable, so you can start small and grow over time.
In this guide, we explore the top ERP system examples for 2026 and explain how to choose the right one for your business.
TL;DR: Top ERP Systems at a Glance
- CollabCRM: An all-in-one business operating system to manage sales CRM, people, projects, recruitment, and operations
- Odoo: Ideal for SMBs that need flexibility and customization
- Zoho: Suited for growing teams that want AI-driven insights within one platform
- SAP: Designed for large enterprises handling complex and global processes
- Microsoft Dynamics 365: A strong choice for businesses deeply integrated with Microsoft tools
- NetSuite: Well-suited for mid-sized and scaling companies looking for a unified cloud platform
- Workday: Built for organizations with advanced HR and finance requirements
- Productive: Tailored for creative, consulting, and digital agencies
- Oracle ERP: Built to support large organizations with deep and scalable ERP needs
- Sage ERP: A practical option for SMBs seeking a simple ERP with strong financial controls
What is an ERP System?
ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning. An ERP system is software that helps businesses manage their core operations in one place.
It connects different departments like sales, finance, HR, and projects into a single system. Instead of using separate tools, teams work on the same platform with shared data.
An ERP system stores information in a centralized database. This ensures data is accurate, updated, and accessible in real time. It reduces manual work and minimizes errors caused by duplicate entries.
Modern ERP systems are usually cloud-based. They can be accessed from anywhere and scale as the business grows. Most ERPs are modular, so companies can choose only the features they need.
For business owners and decision makers, an ERP system provides better control, clearer insights, and faster decision-making.
What are the Key Features of an ERP System?
Key ERP features include CRM, HR management, project tracking, financial management, and real-time reporting. A good ERP system covers all critical business functions in one platform. These features help teams work efficiently and give leaders full visibility into operations.
Below are the core features most modern ERP systems offer.
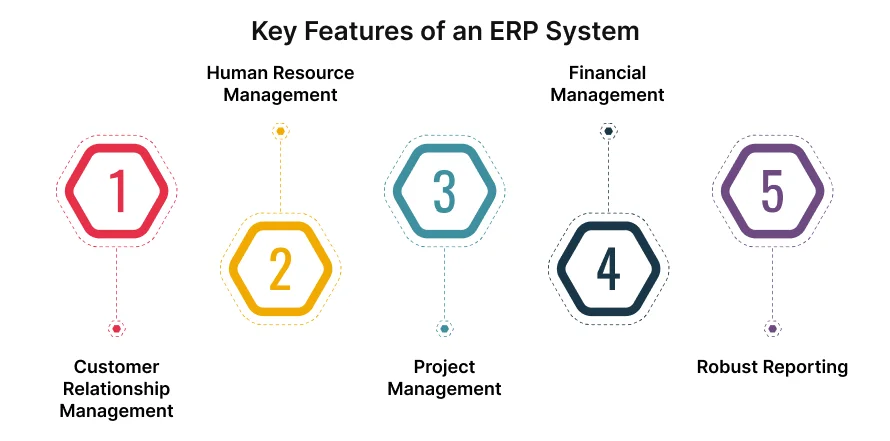
Customer Relationship Management
A CRM helps manage customer relationships and sales activities. It tracks leads, deals, customer interactions, and follow-ups in one place.
With CRM built into the ERP, sales teams have access to real-time customer data. This improves conversion rates and customer retention.
Human Resource Management
A human resource management system manages employee records, payroll, attendance, and performance. It simplifies hiring, onboarding, and compliance.
An integrated HR module ensures employee data stays accurate and up to date across the organization.
Project Management
Project management features help plan, track, and deliver work on time. Teams can assign tasks, set deadlines, and monitor progress.
When projects connect with finance and CRM, businesses gain better control over costs and resource usage.
Financial Management
This module handles accounting, budgeting, invoicing, and expense tracking. It provides a clear view of cash flow and financial health.
Automated processes reduce manual errors and improve reporting accuracy.
Robust Reporting
ERP reporting brings data from all departments into one dashboard. Leaders can track KPIs, generate reports, and make data-driven decisions.
Real-time insights help businesses respond faster to changes.
What are the Benefits of ERP Systems?
ERP systems help businesses work faster, reduce errors, and gain full control over operations. They offer clear advantages for business owners and decision makers. By connecting people, data, and processes, they help businesses run more smoothly and scale with confidence.
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
ERP systems automate repetitive tasks and reduce manual work. Teams spend less time on data entry and more time on high-value work.
Centralized Data and Real-Time Reporting
All business data lives in one system. This improves data accuracy and gives leaders real-time visibility into performance.
Cost Reduction
By reducing errors, duplicate tools, and manual processes, ERP systems help lower operational costs over time.
Improved Collaboration
Teams work from the same data and custom workflows. This improves communication and reduces delays between departments.
Enhanced Customer Service
With complete customer data in one place, teams can respond faster and deliver better service experiences.
Compliance and Risk Management
ERP systems support audit trails, access controls, and compliance requirements. This helps reduce operational risks.
Scalability and Flexibility
Modern ERP systems grow with your business. You can add users, features, and modules as your needs change.

Top 10 ERP Systems Examples for 2026
The top ERP system examples include platforms that combine finance, people, projects, and reporting into scalable, cloud-based solutions.
Below are some of the most widely used and trusted ERP system examples for 2026. Each option serves different business sizes and needs, from SMBs to large enterprises.
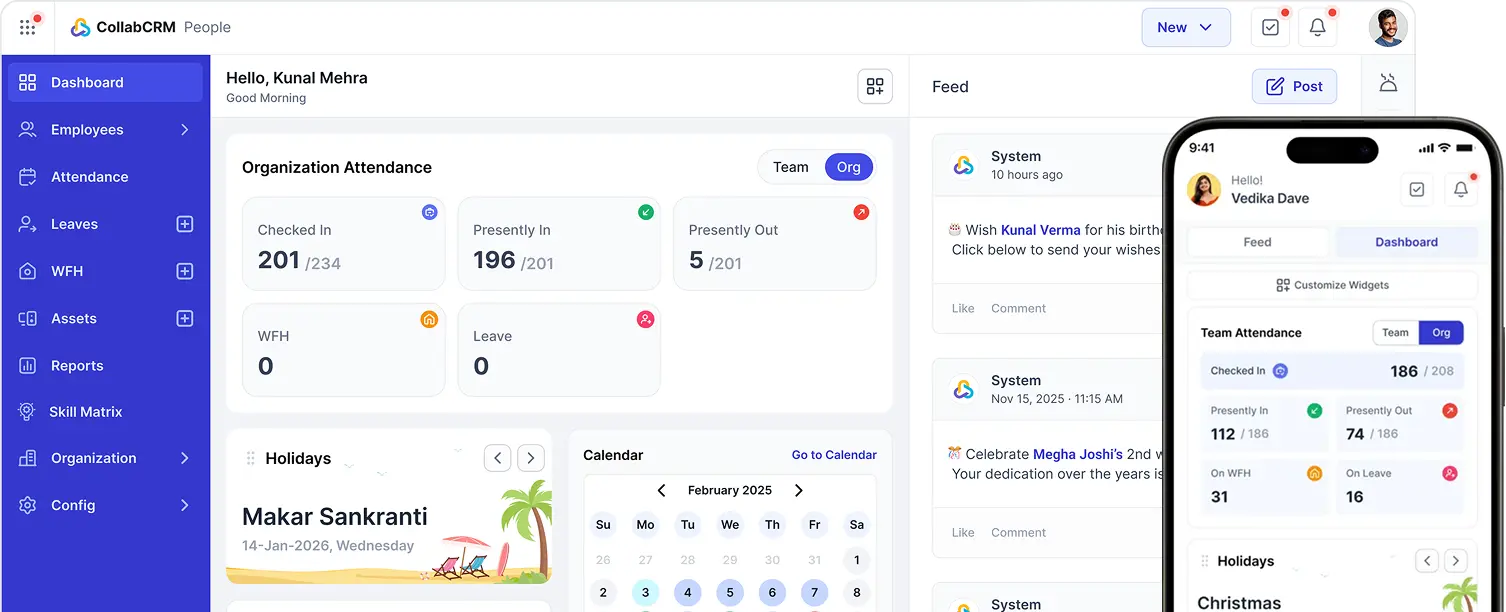
1. CollabCRM
CollabCRM is a modern, all-in-one business operating system that goes beyond an ERP, built for growing businesses, SMBs, and enterprises. It focuses on simplicity, visibility, and connected workflows.
It combines key modules like sales CRM, people management, project management, and reports in one place. The platform is easy to set up and use, so teams can start seeing value fast. CollabCRM also offers built-in collaboration across individual modules and customizable dashboards, making it useful for teams that need connected workflows across sales, operations, employee management, and revenue leakage identification.
People Management Module – ERP Control of Human Capital and Resources
In an ERP system, people are the most valuable resource. CollabCRM’s People Management module centralizes the entire employee lifecycle in a single system.
It manages attendance, leaves, organization structure, and role ownership without spreadsheets. Leaders get real-time visibility into who is working, where they are assigned, and how teams are structured.
The Global Skill Matrix helps match the right talent to the right work. This improves delivery quality and resource utilization. The IT Asset Tracker adds accountability by tracking laptops, devices, ownership, and warranties.
During employee exits, the Exit Dependency Manager protects business continuity. It highlights linked assets, responsibilities, and access points before offboarding. This makes CollabCRM a strong ERP for workforce control and risk reduction.
Project Management Module – ERP Execution and Delivery Control
This module acts as the execution engine of CollabCRM. It ensures projects are delivered on time, within scope, and with full cost visibility.
Managers can see daily allocations and occupancy reports to understand actual workload distribution. This helps prevent overbooking and underutilization of resources, enabling resource planning.
Kanban boards support agile execution with tasks, sprints, and backlogs. Integrated work logs ensure accurate time tracking and billing.
Financial reports compare planned hours with actual hours spent. This helps identify revenue leakage early. Public timesheet links allow clients to view progress without platform access, improving transparency and trust.

Sales CRM Module – ERP Control of Revenue and Client Lifecycle
In CollabCRM, CRM focuses on managing company resources, not just contacts. Sales, delivery, and invoicing work from the same data.
Deals closed in the CRM move directly into active projects. This ensures delivery teams follow the exact scope, timelines, and commitments promised during sales.
The invoice dashboard tracks overdue payments and cash flow health. Aging reports help prioritize collections and reduce delays.
Goal tracking allows leadership to set and monitor targets for leads, deals, and collections. This keeps revenue planning measurable and accountable, which is critical in an ERP system.
Recruitment Module – ERP-Driven Talent Acquisition
The Recruitment module functions as a built-in ATS within the ERP. It manages hiring from job posting to onboarding.
Recruitment funnels show where candidates drop off and how efficient hiring teams are. Custom evaluation criteria ensure fair and consistent candidate assessments.
Once a candidate is selected, offer letters are generated with one click. Digital signing speeds up approvals. The candidate record then flows directly into the People Management module.
This tight integration helps businesses scale teams faster without data duplication or manual handovers.
Reporting Module – Centralized ERP Intelligence Layer
The Reporting module is the decision engine of CollabCRM. It pulls data from all modules into one centralized view.
Leaders can access employee performance reports, deal conversion trends, productivity insights, and time-spent analysis. These reports replace fragmented spreadsheets and manual tracking.
Operational reports highlight risks early, such as low engagement, attendance issues, or rising exit trends.
With real-time, data-driven insights, CollabCRM enables faster and more confident decisions. This makes it a reliable ERP system and a true single source of truth for growing IT enterprises.
2. Odoo ERP
Odoo is known for flexibility and customization. It is open source and modular, letting you pick only the apps you need. Whether it is accounting, CRM, inventory, HR, or e-commerce, you can add or remove modules as your business changes.
Odoo offers strong community support and a marketplace with many extensions. Its wide range of features makes it suitable for SMBs with evolving needs.
Key features of Odoo ERP:
- Modular apps for sales, finance, HR, and inventory
- Customizable workflows
- Strong community and integrations
- Suitable for SMBs and mid-sized businesses
3. Zoho ERP
Zoho ERP is built with tight integration across billing, operations, and finance. It includes native AI features such as voice assistance, predictive insights, and anomaly detection. Zoho also offers built-in banking connections and compliance tools, reducing the need for additional setup. This makes Zoho’s ERP platform easier to manage and more modern than legacy systems.
Zoho ERP Key features:
- CRM, finance, HR, and operations tools
- Cloud-based and user-friendly
- Strong automation capabilities
- Cost-effective for small businesses
4. SAP ERP
SAP is one of the most established ERP systems, especially for large enterprises with complex needs. Its flagship system (SAP S/4HANA) runs on an in-memory database for fast processing and real-time analytics.
SAP handles massive data volumes and deep industry-specific processes in finance, supply chain, manufacturing, and customer operations. The platform is highly scalable and works across global teams.
Key features of SAP ERP:
- Advanced financial and supply chain management
- Strong analytics and reporting
- Industry-specific solutions
- Best for large enterprises with complex needs
5. Microsoft Dynamics 365
Microsoft Dynamics 365 blends ERP with CRM and ties closely to Microsoft products like Office 365, Teams, and Power BI. This makes it powerful for businesses already using Microsoft tools. Dynamics 365 supports finance, sales, operations, and reporting, while its integration with Azure cloud and AI services adds modern analytics and automation.
Key features:
- Seamless integration with Microsoft 365
- Finance, sales, and operations modules
- AI-powered insights
- Suitable for mid to large businesses
6. NetSuite ERP
NetSuite, owned by Oracle, is one of the leading cloud-based ERPs for fast-growing businesses. It offers strong financial management, CRM, inventory, and e-commerce support in a single platform. Its cloud-native architecture gives real-time visibility and unified workflows.
NetSuite is popular with mid-sized companies that have outgrown basic accounting software but need one system for global operations
Key features:
- Financial management and reporting
- CRM and e-commerce support
- Real-time dashboards
- Popular among scaling SMBs and enterprises
7. Workday
Workday specializes in financial management and human capital management (HCM). It has a modern, cloud-first design and strong automation for payroll, talent, planning, and analytics. Workday is widely used by larger organizations focused on workforce planning and finance alignment. Its secure architecture also supports compliance in regulated sectors.
Key features:
- HR, payroll, and workforce planning
- Financial management and analytics
- Cloud-based architecture
- Ideal for people-centric organizations
8. Productive
Productive is tailored for agencies and service-based companies. It combines project management, budgeting, time tracking, and CRM in a single platform. Teams can plan projects, monitor costs, and track profitability easily. It’s a simpler alternative to larger ERP systems for teams that need strong project control and workforce visibility without heavy IT overhead.
Key features:
- Project management and budgeting
- Time tracking and profitability reports
- CRM for sales pipelines
- Best for creative and digital agencies
9. Oracle ERP
Oracle Cloud ERP is a robust, enterprise-grade system covering financials, procurement, project management, HCM, and supply chain. It includes built-in analytics and reporting and is designed for high scalability, security, and complex global operations. Oracle’s ERP is widely recognized for supporting large multinational companies with deep financial and operational requirements.
Key features:
- Financials, procurement, and risk management
- AI-driven insights
- High scalability and security
- Designed for large and complex organizations
10. Sage ERP
Sage ERP focuses on small and mid-sized businesses. It includes finance, payroll, inventory, and operations management. Sage systems are easy to use and implement, with features tailored to simplify accounting and business processes. They help teams reduce manual tasks and improve visibility without high cost or complexity.
Key features:
- Accounting and financial management
- Payroll and compliance support
- Easy-to-use interfaces
- Strong presence in SMB markets
How To Implement an ERP System? (Step-by-Step)
A successful ERP implementation requires clear ownership, realistic planning, user adoption, and ongoing optimization. It is a strategic process. A clear plan helps reduce risks, control costs, and ensure user adoption.
Step 1: Get Leadership Support
ERP implementation needs strong backing from leadership. Executives should align on goals, budget, and success metrics from the start. Their support helps remove roadblocks and keeps teams accountable.
Step 2: Choose a Project Owner
Assign one person to lead the implementation. This owner coordinates with vendors, manages timelines, and ensures teams stay aligned. Clear ownership prevents confusion and delays.
Step 3: Set Clear Timelines
Break the implementation into phases with realistic deadlines. Avoid rushing the process. Clear milestones help track progress and manage expectations.
Step 4: Train Users & Manage Change
Provide hands-on training for teams. Explain how the ERP improves daily work. Ongoing support reduces resistance and improves adoption.
Step 5: Test, Review & Improve
Test the system before full rollout. Gather feedback, fix issues, and optimize workflows. Continuous improvement ensures long-term success.
How to Choose the Right ERP for Your Business?
Businesses should choose an enterprise resource planning tool that fits their current needs, budget, and future growth.
Needs Assessment
Start by identifying your business challenges. List the processes you want to improve, such as sales tracking, accounting, HR, or project management. Involve key stakeholders so real needs are captured early.
Market Research
Compare ERP systems that match your business size and industry. Look at product capabilities, pricing models, and customer reviews. Shortlist options that align with your priorities.
Technical Analysis
Check how the ERP fits with your existing tools. Review cloud access, data security, customization options, and scalability. Make sure the system can grow with your business.
Vendor Check
Evaluate the vendor’s reputation and support. Look at implementation help, training, updates, and long-term reliability. A strong vendor partnership reduces risk after launch.
Final Thoughts
Choosing the right ERP system is a long-term decision that impacts every part of your business. The right platform helps streamline operations, improve visibility, and support smarter decision-making. For business owners and SMB leaders, an ERP should simplify work, not add complexity.
In 2026, modern ERP systems are flexible, cloud-based, and built to scale. The key is to focus on your actual business needs, team readiness, and future growth. When the fit is right, an ERP becomes a strong foundation for sustainable growth.
Why CollabCRM Is the Right ERP for Growing Businesses?
CollabCRM is built for businesses that want an all-in-one ERP without the learning curve of traditional systems. It brings SalesCRM, people management, project management, recruitment, and reporting into one connected platform.
With simple setup, right collaboration, intuitive workflows, and clear dashboards, CollabCRM helps teams work faster while giving leaders full control and visibility. For growing businesses and SMBs, it delivers exactly what an ERP should: clarity, efficiency, and scalability.
FAQs
An ERP system is software that manages core business operations in one platform. It connects sales, finance, HR, projects, and reporting. This helps businesses work with accurate, real-time data.
Yes. Modern ERP systems are built for SMBs. They replace multiple tools, reduce manual work, and improve visibility. This makes daily operations easier to manage.
Implementation time depends on business size and complexity. For SMBs, it can take a few weeks. Larger organizations may need several months.
Focus on your business needs, ease of use, scalability, and integrations. Also, check vendor support, training, and long-term costs.
For most businesses, yes. Cloud ERPs are easier to maintain, scale faster, and offer remote access. They also reduce upfront infrastructure costs.
Yes. A good ERP replaces CRMs, HR tools, project software, and reporting tools. This reduces costs and data silos.
CollabCRM works as a Business Operating System and a modern ERP alternative. It combines people management, projects, sales, hiring, and reporting into one platform. It acts as a single source of truth for IT and service-based businesses.
Costs vary by vendor, features, and users. SMB-focused ERP systems are usually subscription-based and more affordable than traditional enterprise ERPs.
Poor planning and low user adoption. Clear goals, leadership support, and proper training help avoid these issues.