Project timelines are no longer just planning documents. For IT teams, they are decision tools.
As projects grow more complex, teams deal with changing requirements, shared resources, and tight delivery expectations. A missed dependency or a delayed task can quickly impact cost, quality, and customer trust.
This is where timelines in project management become critical.
A well-managed timeline helps teams understand what needs to happen, when it needs to happen, and who is responsible. It brings clarity across engineering, QA, operations, and leadership. More importantly, it allows teams to adapt without losing control when plans change.
This guide explains project timeline management in a practical and structured way. You will learn what timelines are, why they matter in IT projects, and how to build, track, and improve them. The focus is on real-world execution, not theory.
Whether you are a project manager planning delivery or a decision-maker looking for predictability, this guide will help you manage timelines with confidence.
TL;DR: Project Timeline Management Under Minutes
- Project timeline management aligns tasks, dependencies, milestones, and ownership to deliver projects on time
- IT projects require active timeline management due to changing requirements, dependencies, and resource constraints
- How to make timeline for project: clear scope definition, task breakdown, dependency mapping, and milestone planning
- Core timeline components include task sequencing, ownership clarity, and built-in buffers
- Proven techniques include Gantt charts, Kanban boards, Agile & Hybrid timelines, and Rolling Wave Planning
- Timelines stay on track through continuous monitoring, controlled changes, and clear communication
- Timeline performance is measured using on-time delivery, schedule variance, cycle time, and lead time
- Integrated tools like CollabCRM support real-time visibility, resource alignment, and adaptable timelines
What Is Project Timeline Management?
Project timeline management is the process of planning, organizing, and tracking project work over time to ensure timely delivery. It shows how tasks, milestones, and responsibilities are sequenced from the start of a project to its completion.
In IT projects, work flows across multiple teams and stages. A project timeline brings this work into a single, time-based view. It helps teams understand what needs to happen next, what depends on earlier tasks, and how delays can impact delivery.
A project timeline is different from other planning views. A timeline focuses on the order and timing of work. A project schedule adds detailed dates and resource assignments. Together, they support planning at different levels.
What Does a Project Timeline Include?
A project timeline is built using a few core elements.
- Tasks: The individual pieces of work required to complete the project.
- Durations: Estimated time needed to complete each task.
- Dependencies: Relationships between tasks that determine execution order.
- Milestones: Key checkpoints that indicate progress or completion.
- Ownership: Clear responsibility assigned to roles or individuals.
When these elements are clearly defined, a project timeline becomes easier to track, adjust, and communicate across teams.
Why Is Project Timeline Management Critical for IT Projects?
IT projects are rarely linear. Teams work across functions, priorities shift, and dependencies span development, testing, and deployment. The overload of IT service management is another challenge.
Under such circumstances, it becomes difficult to understand how work fits together or how delays in one area affect the rest of the project, without a clear timeline.
Project timeline management creates structure in this complexity. It gives teams a shared view of work over time, helping them plan realistically and respond to change without losing control.
Business Impact of Poor Project Timeline Management
When project timelines are unclear or poorly managed, problems tend to spread quickly. Small delays grow into larger issues that affect delivery, cost, and team morale.
Missed Deadlines
Unclear task order causes teams to start work without required inputs. Dependencies surface late, leading to delays that impact the entire project.
Higher Costs
Rushed execution leads to mistakes and rework. Teams spend more time and effort fixing issues that could have been avoided with better planning.
Loss of Trust
Frequent timeline changes make delivery dates unreliable. Stakeholders find it difficult to plan and gradually lose confidence in the project.
Team Burnout
Constant firefighting increases stress and fatigue. Teams focus on reacting to problems instead of delivering quality work.
Benefits of Effective Project Timeline Management
Strong timeline management improves how projects are planned, tracked, and delivered.
Predictable Delivery
Clear timelines help teams commit to realistic deadlines and meet them consistently.
Better Decisions
Visible progress allows leaders to identify risks early and adjust plans when needed.
Clear Ownership
Defined timelines and responsibilities improve accountability across teams.
Stronger Teamwork
Shared timelines improve coordination and reduce friction between teams.
How to Create a Project Timeline? (Step-by-Step)
A project timeline works by breaking down a project into manageable steps and arranging them over time. Each step builds on the previous one, helping teams plan workload logically and track progress as execution begins.
When followed correctly, this step-by-step approach reduces uncertainty and improves delivery control.
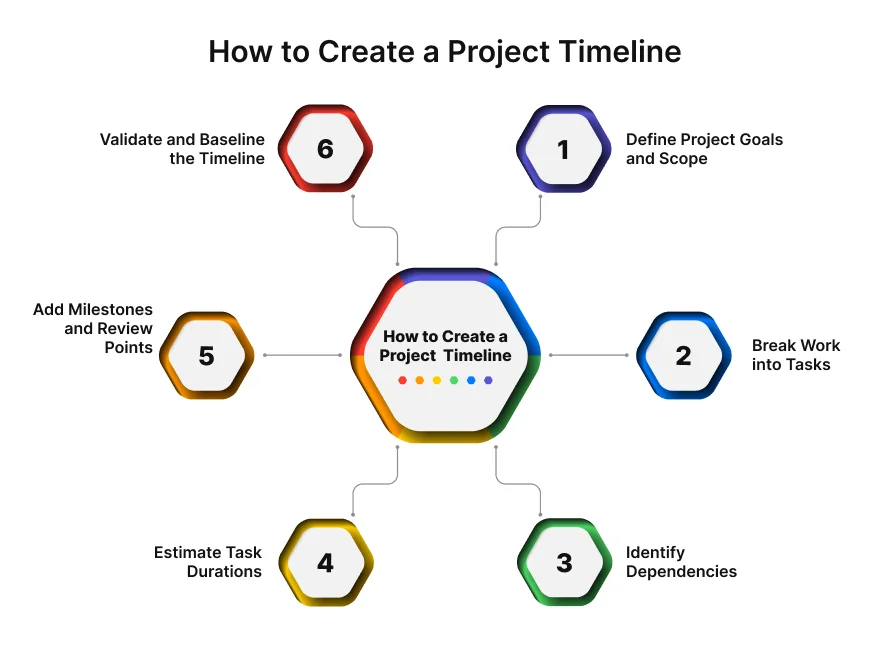
Step 1: Define Project Goals and Scope
Every timeline starts with clarity. Project goals define what success looks like, while scope outlines what is included and what is not.
Clear goals help teams align timelines with business priorities. A well-defined scope prevents unplanned work from slipping into the timeline later. Without this clarity, timelines quickly become unrealistic.
Step 2: Break Work into Tasks
Once goals are clear, the next step is to break the project into smaller tasks. This workforce planning is often done using a Work Breakdown Structure.
Breaking work into tasks makes estimation easier and improves execution. Tasks should be specific, measurable, and actionable. Well-defined tasks reduce confusion and make progress easier to track.
Step 3: Identify Dependencies
Not all tasks can start at the same time. Some depend on the completion of others.
Identifying dependencies helps teams understand task order and avoid bottlenecks. It also highlights critical paths where delays can directly impact delivery. Overlooked dependencies are one of the most common causes of timeline slippage.
Step 4: Estimate Task Durations
After tasks and dependencies are identified, teams estimate how long each task will take.
Estimates should be based on past project data, team experience, and known risks. Overly optimistic estimates increase the chance of delays, while realistic estimates improve timeline accuracy.
Step 5: Add Milestones and Review Points
Milestones mark important checkpoints in the project timeline. They help teams track progress and validate outcomes.
Review points allow stakeholders to assess progress and make decisions. Regular milestones reduce the risk of surprises late in the project.
Step 6: Validate and Baseline the Timeline
Before execution begins, the timeline should be reviewed with all involved teams.
Validation ensures tasks, durations, and dependencies are realistic. Once approved, the timeline becomes the baseline used to measure progress and manage changes during the project.

What Are the Key Components of an Effective Project Timeline?
An effective project timeline is built on a few core components that work together. When these components are clearly defined, timelines become easier to manage, update, and communicate throughout the project.
Tasks and Ownership
Tasks represent the individual units of work required to complete a project. Each task should have clear ownership so there is no confusion about responsibility.
Assigning ownership helps teams stay accountable and reduces delays caused by unclear expectations. It also makes it easier to track progress and address issues quickly.
Dependencies and Sequencing
Dependencies define how tasks are connected and in what order they should be completed. Proper sequencing ensures work progresses smoothly from one stage to the next.
When dependencies are mapped early, teams can avoid blockers and plan work more effectively. Clear sequencing also helps identify critical tasks that have the greatest impact on delivery timelines.
Milestones and Deliverables
Milestones mark important points in the project timeline. They represent the completion of key phases or deliverables.
Using milestones helps teams measure progress and gives stakeholders clear checkpoints to review outcomes. They also make large projects easier to manage by breaking them into meaningful stages.
Buffers and Contingencies
Buffers account for uncertainty and risk. They provide extra time for tasks that may take longer than expected.
Including contingencies in the timeline helps teams handle unexpected delays without disrupting the entire project. This makes timelines more realistic and resilient.
What Are the Best Project Timeline Management Techniques?
Like different projects follow different project management methodologies, different projects need diverse timeline techniques. The right approach depends on task complexity, dependencies, and how often requirements change. For IT projects, teams often combine multiple techniques to maintain both structure and flexibility.
Kanban Boards for Timeline Visibility
Kanban boards focus on visualizing work as it moves through different stages, such as to do, in progress, and done.
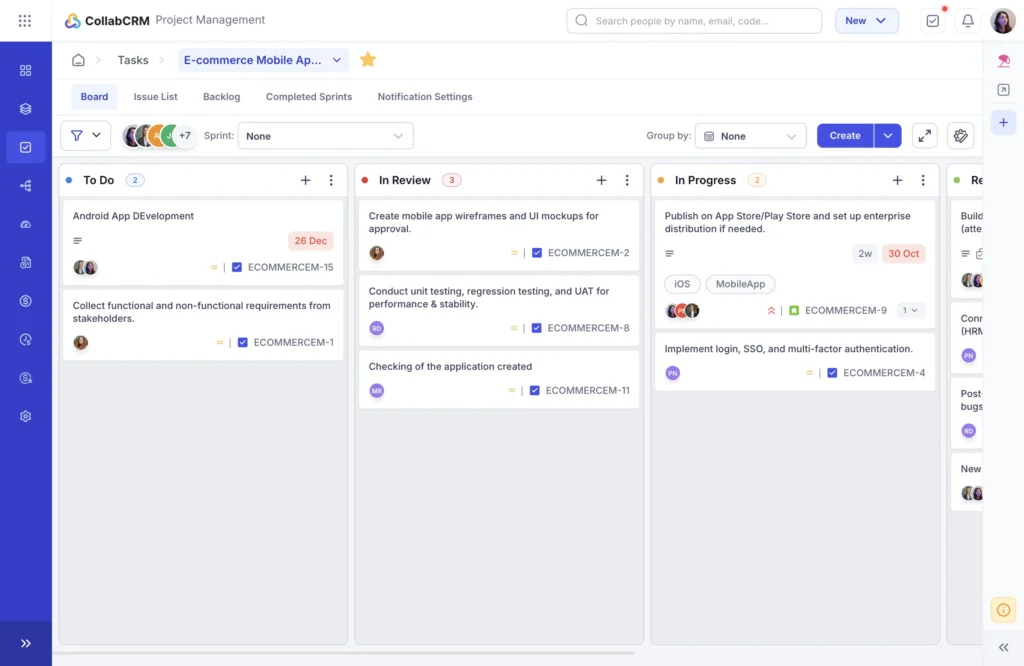
They help teams see bottlenecks early and understand where work is slowing down. Kanban boards also support real-time tracking against planned dates, making it easier to adjust timelines as priorities change. This technique is ideal for iterative, support-driven, or ongoing IT work where tasks flow continuously.
Gantt Charts
Gantt charts provide a time-based view of the entire project. Tasks are plotted against a calendar, showing start dates, end dates, and dependencies.
This technique works well for dependency-heavy IT projects where sequencing matters. It helps teams understand how delays in one task can impact others. Gantt charts are also useful for stakeholder alignment because they present timelines in a clear, easy-to-read format.
Agile and Hybrid Timelines
Agile timelines are built around short, time-boxed sprints rather than fixed long-term plans. Work is planned in cycles, with regular reviews and adjustments.
Hybrid timelines combine Agile flexibility with traditional planning. Teams may use sprints for execution while maintaining a high-level project timeline for leadership and clients. This approach works well for complex IT programs with evolving requirements.
Rolling Wave Planning
Rolling wave planning focuses on detailed planning for near-term work while keeping future phases at a higher level.
As the project progresses, upcoming phases are planned in more detail. This technique reduces estimation errors and allows teams to adapt timelines as new information becomes available.
Scenario-Based Timeline Planning
Scenario-based planning prepares teams for different possible outcomes. Timelines are created for best-case, expected, and worst-case scenarios.
This approach helps teams anticipate risks and respond faster when issues arise. It also supports better decision-making during changes by showing the impact of different options on delivery dates.
How Do Project Managers Track and Control Timelines?
Creating a project timeline is only the starting point. What keeps a project on track is how well the timeline is monitored, adjusted, and communicated as work progresses. For IT projects, where priorities can shift quickly, active timeline control is critical.
1. Tracking Progress
Project managers track progress by comparing planned work with actual execution. This includes monitoring task completion, milestone achievement, and workload distribution.
Regular status updates help surface delays early. When progress is visible, teams can address issues before they affect the entire timeline. Consistent tracking also creates a reliable data trail that improves future planning and estimates.
2. Managing Timeline Changes
Timeline changes are common in IT projects due to evolving requirements, technical dependencies, or resource availability. The key is not avoiding change, but controlling it.
Effective managers assess the impact of changes before approving them. They evaluate how a change affects dependencies, milestones, and delivery dates. Controlled change management prevents small adjustments from turning into major delays.
3. Communicating Timeline Status
Clear communication keeps everyone aligned. Project managers share timeline updates with stakeholders in a simple and consistent format.
This includes what is on track, what is at risk, and what actions are being taken. Transparent communication builds trust and reduces last-minute surprises. It also helps decision makers act faster when support or prioritization is needed.
What Tools Support Project Timeline Management?
Project timeline management becomes significantly easier when supported by the right tools. For IT teams, tools need to balance structure, flexibility, and visibility across tasks, people, and timelines.
1. CollabCRM
CollabCRM supports project timeline management by treating timelines as part of a larger operational system plan, not as mere static plans. For IT teams, this means timelines stay connected to tasks, people, and delivery commitments throughout the project lifecycle.
Instead of relying on disconnected collaboration tools, teams manage planning, execution, and tracking in one place, which helps reduce delays caused by misalignment and poor visibility.
Key Project Management Features of CollabCRM:
1. Defined Project Timelines
Project start and end dates are set during setup and remain visible across project views. This keeps delivery expectations clear for both execution teams and decision makers.
2. Milestone Tracking
Custom milestone statuses can be created to reflect real delivery stages. These milestones act as progress markers and help teams review timelines at critical points.
3. Kanban Boards for Execution Visibility
Work is visualized across stages, making it easier to spot bottlenecks, stalled tasks, or overloaded resources. This supports faster timeline corrections.
4. Sprint-Based Planning
Teams can plan work in time-bound sprints with defined goals. Tasks move from backlog to active execution, helping teams manage timelines in iterative delivery models.
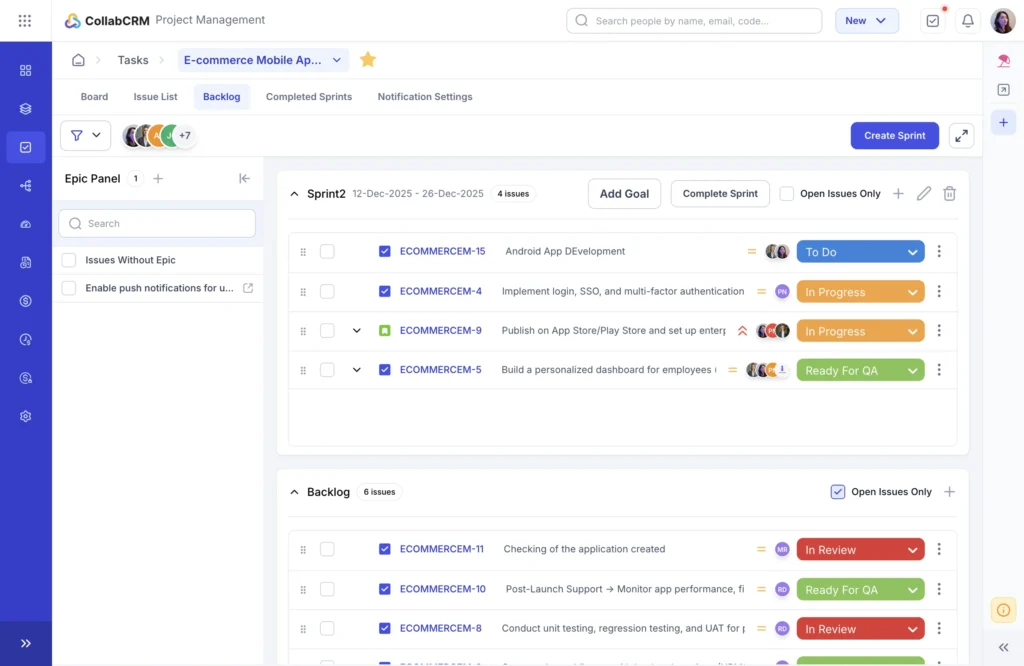
5. Project Timeline History
Every update to tasks or resources is logged automatically. This creates clarity around when and why timeline shifts occurred.
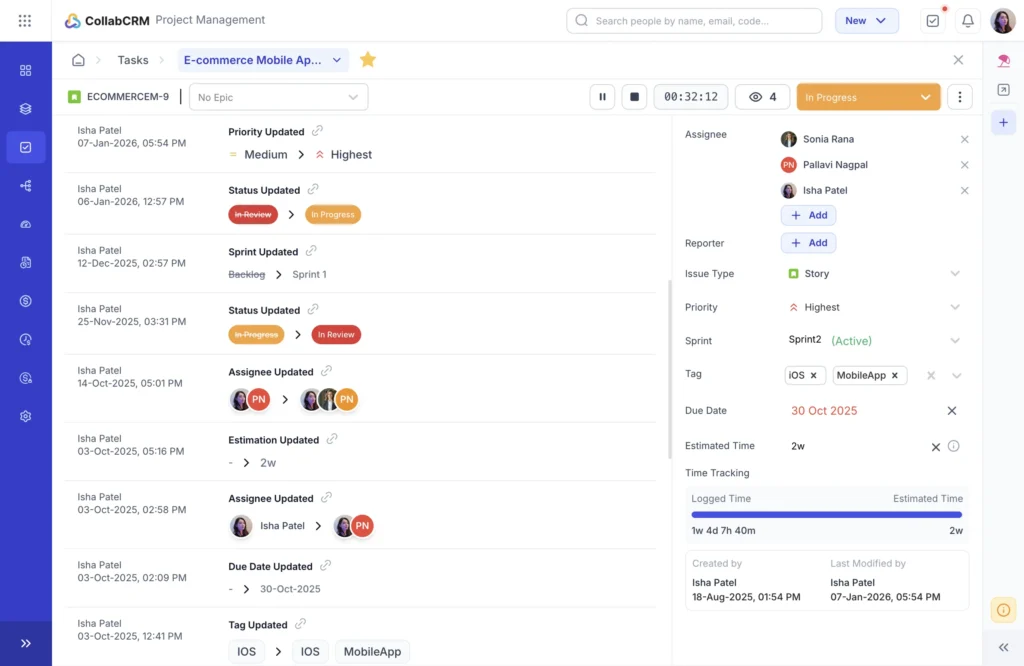
Together, these features help teams maintain timelines that are realistic, transparent, and adaptable. This is especially valuable for IT projects with multiple dependencies, parallel workstreams, and evolving requirements.
2. Asana
Asana is commonly used for task-based timeline planning. It supports visual timelines, task dependencies, and progress tracking.
Teams often use Asana to manage structured project plans and collaborate on task updates. It works well for teams that prefer a lightweight, task-first approach to timeline management.
3. Jira
Jira is widely used by software development teams working in Agile environments. It supports sprint planning, backlog tracking, and release timelines.
Jira timelines are especially useful for managing iterative development work, tracking dependencies between issues, and coordinating across engineering teams.
What Metrics Measure Project Timeline Performance?
Project timeline performance is measured using four core metrics: on-time delivery rate, schedule variance, cycle time, and lead time. Together, these metrics show whether work is being completed as planned, how far the project is deviating from the schedule, and how efficiently tasks move from start to finish.
For IT projects, tracking these metrics helps teams balance speed with reliability and maintain predictable delivery timelines.
On-Time Delivery Rate
This metric shows how often tasks or milestones are completed by their planned dates. A low on-time rate signals unrealistic planning or frequent disruptions.
Schedule Variance
Schedule variance compares planned progress with actual progress. It helps identify whether the project is running ahead or behind the original timeline.
Cycle Time
Cycle time measures how long it takes to complete a task once work starts. Tracking this helps teams spot inefficiencies and improve execution speed.
Lead Time
Lead time covers the total time from task creation to completion. This metric provides a broader view of how quickly work moves through the system.
Timeline metrics work best when used for improvement, not blame. Comparing planned and actual timelines helps teams spot recurring delays, resource gaps, and process issues. Over time, this leads to more accurate planning and more predictable delivery.
Project Timeline: Common Pitfalls & Best Practices
Effective timeline management is not just about building a plan. It is about how that plan is used, reviewed, and adapted as the project moves forward. Many IT project delays come from avoidable mistakes that can be corrected through consistent best practices.
1. Avoid Treating Timelines as Static Plans
Timelines should evolve as projects progress. When timelines are treated as fixed documents, teams stop updating them as conditions change. This leads to outdated plans and late surprises.
- Best practice: Review and adjust timelines regularly based on real progress and new information.
2. Account for Task Dependencies Early
Ignoring dependencies between tasks often results in work being blocked unexpectedly. When one delayed task impacts several others, the entire timeline slips.
- Best practice: Identify and map dependencies during planning and revisit them whenever scope or priorities change.
3. Plan Around Real Resource Capacity
Overloading team members is a common cause of missed deadlines and burnout. When timelines are built without considering availability, delivery becomes unrealistic.
- Best practice: Align timelines with actual team capacity using historical workload and current availability data.
4. Maintain Timely Progress Updates
Delayed or inconsistent status updates make it difficult to identify risks early. By the time issues are visible, recovery options are limited.
- Best practice: Encourage frequent, lightweight updates that reflect real progress against the timeline.
5. Communicate Changes Clearly and Early
Poor change communication erodes trust and creates confusion across teams and stakeholders. Timeline changes that are not clearly explained often lead to misaligned expectations.
- Best practice: Communicate timeline changes as soon as they occur, along with their impact and next steps.
6. Align Timelines with Business Priorities
Timelines that are disconnected from business goals often fail to deliver real value. Teams may hit dates but miss outcomes.
- Best practice: Ensure project timelines support broader business objectives and adjust priorities when needed.
7. Use Data to Improve Future Timelines
Relying only on assumptions leads to repeated estimation errors.
- Best practice: Use historical project data to refine estimates and improve timeline accuracy over time.
By avoiding all these common pitfalls and applying these best practices, IT leaders can create timelines that are realistic, transparent, and resilient to change.
Conclusion
Project timeline management helps IT teams turn plans into predictable outcomes. When timelines are actively tracked, adjusted, and clearly communicated, teams reduce delays, improve coordination, and deliver with confidence. Strong timeline practices make execution more reliable and less reactive.
CollabCRM helps teams manage timelines as part of daily execution, not as static plans. By connecting tasks, milestones, Kanban boards, and resource visibility in one system, it enables real-time tracking and faster adjustments. This integrated approach supports realistic timelines and consistent delivery across IT projects.
FAQs
A project timeline is a visual plan that shows when project tasks start and end, how they are sequenced, and when key milestones are achieved. It helps teams understand the flow of work, track progress over time, and ensure the project stays on schedule.
Project timeline management is the process of planning, tracking, and controlling the sequence and duration of tasks in a project to ensure work is completed on time.
IT projects involve changing requirements, dependencies, and multiple teams. Timeline management helps reduce delays, control costs, and keep stakeholders aligned.
A project timeline typically includes tasks, durations, dependencies, milestones, and task ownership.
A project timeline shows when work happens at a high level, while a project schedule includes detailed task timings, assignments, and execution plans.
Common techniques include Gantt charts, Kanban boards, Agile or hybrid timelines, rolling wave planning, and scenario-based planning.
Project managers track timelines by monitoring task completion, milestone progress, dependencies, and key schedule metrics such as on-time delivery and cycle time.
Key metrics include on-time delivery rate, schedule variance, cycle time, and lead time.
The best tools for project timeline management combine timelines, tasks, dependencies, and resource visibility in one place. While tools like Asana and Jira support task and Agile planning, integrated platforms such as CollabCRM are often preferred for managing end-to-end project timelines in IT teams.